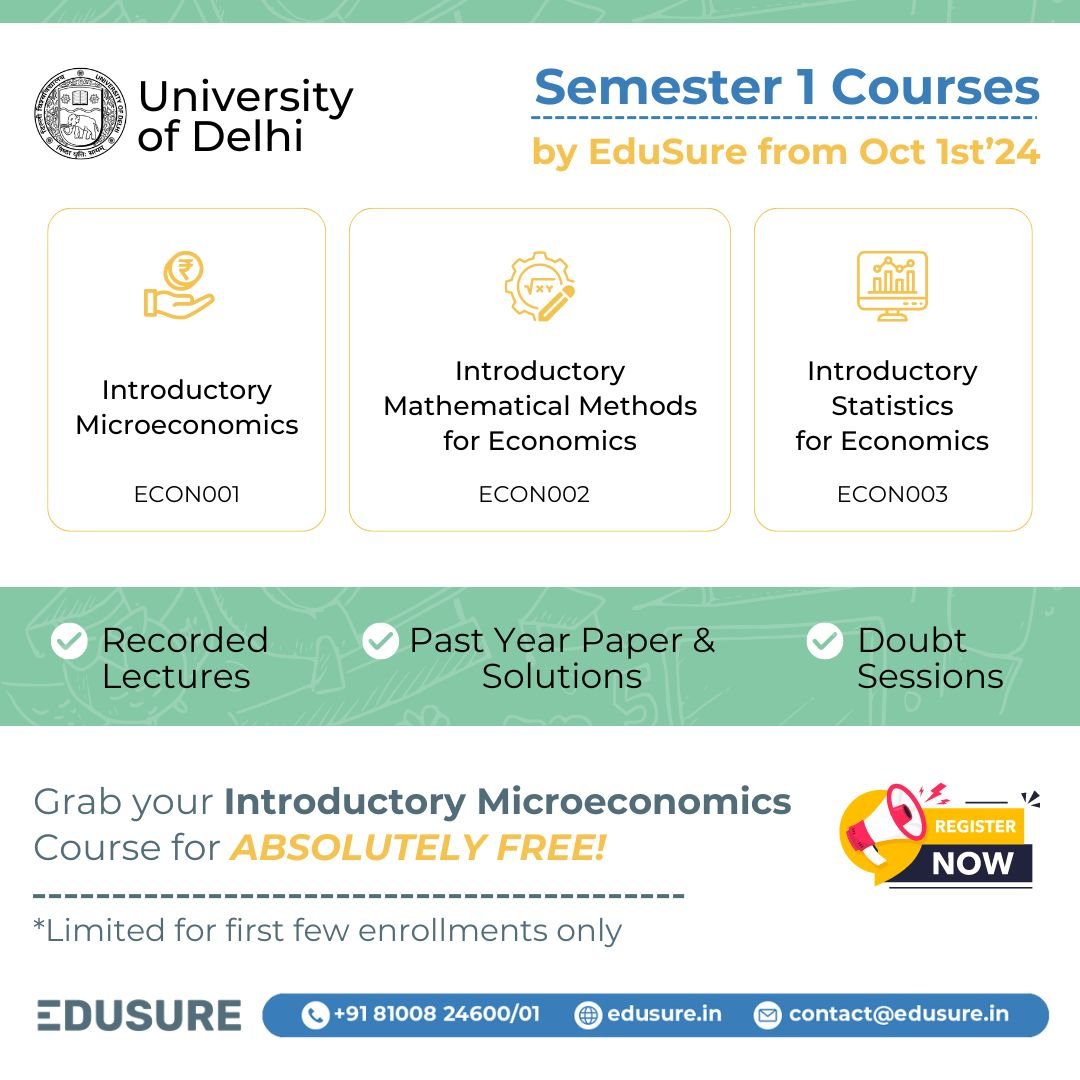
Course Description
Intermediate Microeconomics ( ECON001 ) explores key economic concepts such as consumer behavior, firm production, market structures, and welfare economics. Students will apply mathematical models to analyze market outcomes, efficiency, and government intervention. Ideal for those seeking to deepen their understanding of microeconomic theory and its real-world applications.
Course Starting from 1st October 2024
Recorded Lectures
Past Year Paper & Solutions
Doubt Sessions
Watch Trial Videos
Experience our Intermediate Microeconomics ( ECON001 ) course before enrolling with our exclusive trial classes. These sessions provide a sneak peek into the engaging lectures and interactive teaching methods that define our program.
Part 1 – Chapter 1 | Principles of Economics
Part 1 – Chapter 2 | Thinking like an Economist
Part 1 Chapter 3 Interdependence and Gains From Trade
Marginal Utility of Money
Demand Function
Theory of Demand
Intermediate MicroEconomics Syllabus
Introduction to economic trade-offs
Mankiw, N. G. (2018). Principles of Microeconomics 8th ed.
- Chapter 1 : Ten Principles of Economics (first seven principles of economics )
- Chapter 2 : Thinking Like a Economics
- Chapter 3 : Interdependence and the Gains from Trade
How market works
Mankiw, N. G. (2018). Principles of Microeconomics 8th ed
- Chapter 4 : The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
- Chapter 5 : Elasticity and Its Application
- Chapter 6 : Supply, Demand, and Government Policies
- Chapter 7 : Consumers, Producers, and the Efficiency of Markets
- Chapter 9 : Application : International Trade
Role of government
Mankiw, N. G. (2018). The Principles of Microeconomics 8th ed.
- Chapter 8 : Application : The Costs of Taxation
- Chapter 10 : Externalities
- Chapter 11 : Public Goods and Common Resources
Individual decision and interaction
Dixit, A. K., & Skeath, S. (2015). Games of strategy : Fourth international student edition. WWNorton&Company.
- *Chapter 1
- Chapter 2 ( upto section 2.5 )
Mankiw, N.G. (2018). Principles of Microeconomics 8th ed.
- Chapter 21
Learning Objectives
Unit I: Introduction to Economic Trade-offs
- Understand the basic principles of economics, including scarcity, opportunity cost, and trade-offs.
- Learn how to think like an economist, using models and data to make decisions.
- Explore the concept of interdependence and the gains from trade.
Unit II: How the Market Works
- Analyze the forces of supply and demand and how they determine prices.
- Study elasticity and its importance in understanding market behavior.
- Examine the role of government policies in affecting supply, demand, and market efficiency.
- Understand international trade and its implications for consumers and producers.
Unit III: Role of Government
- Evaluate the costs of taxation and its impact on economic efficiency.
- Analyze externalities and public goods and how government intervention can address market failures.
- Understand common resources and the challenges they present in economic policy.
Unit IV: Individual Decision-Making and Strategic Interaction
- Explore game theory and strategic decision-making in economics.
- Analyze individual preferences and choices within the framework of consumer theory.
Learning Outcomes
Unit I:
- Students will be able to explain basic economic concepts and trade-offs, including opportunity costs and the benefits of trade.
- Students will demonstrate the ability to think like economists, applying economic reasoning to everyday decisions.
Unit II:
- Students will be able to explain how supply and demand interact to determine prices and quantities in a market.
- Students will be able to calculate and interpret elasticities of demand and supply.
- Students will understand the effects of government policies, such as taxes, on market outcomes.
- Students will analyze the benefits and costs associated with international trade.
Unit III:
- Students will be able to evaluate the efficiency and equity implications of different forms of government intervention in the market.
- Students will understand how governments address market failures due to externalities and public goods.
Unit IV:
- Students will apply strategic thinking to economic problems involving multiple decision-makers.
- Students will understand and explain how individual decision-making can lead to different market outcomes, using tools from game theory.
Examination Scheme
Weightage for each unit
Unit I – 15 marks
Unit II – 30 marks
Unit III – 25 marks
Unit IV – 20 marks
This division is flexible and plus/minus 10% of the marks and can be done in each unit, giveb the total is 90.

Past Year Papers
Click to download DU Semester 1 – Introductory Microeconomics ( ECON001 ) past year question papers
FUNTASTIC Faculty from DSE & ISI
Helped 1000’s of students get into their Dream Institute for MA Economics

Samkith Banthia
ISI Alumnus | Eco(H) St Xaviers Kolkata | FRM from GARP | Formerly with Barclay's Bank
Samkith Sir, an alumnus of ISI, transitioned from a successful banking career to pursue his passion for teaching and mentoring aspiring students. With expertise in mathematics and a nurturing demeanor, he stands out as a premier educator, dedicated to guiding students towards academic excellence.

Mahima Banthia
DSE Alumnus | Eco(H) SRCC Delhi | Former Lecturer St Stephen’s College Delhi | NET qualified
In Mahima Ma’am’s class at EduSure, we prioritize logical reasoning and emphasize conceptual understanding, ensuring mastery of macroeconomics. Mahima Ma’am, also handling administrative responsibilities at EduSure, is dedicated to providing the highest quality service to every student.
24*7 Doubt Resolution EduSure Tool For Success
Support & Assistance
Updates on exam registration deadlines and documents required |
Peer WhatsApp and Telegram group for discussions |
24*7 Doubt Resolution all around the year. Student Helpdesk Tool by EduSure. |
Extra classes closer to the exam |
Terms & Conditions
|
|
EduSure Google Reviews
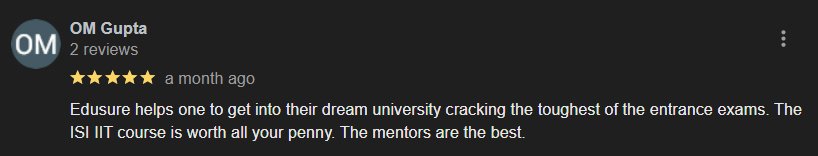
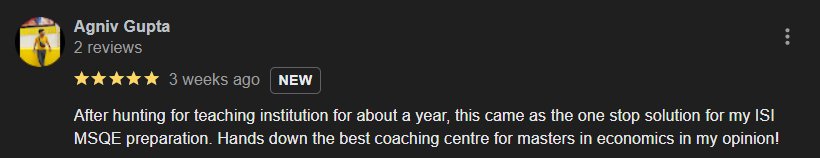
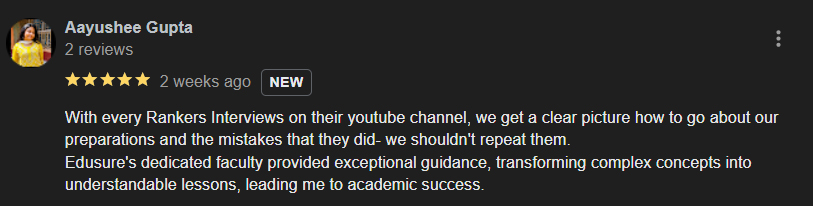



Student Reviews